submitted by jwithrow.
We have been hearing all about how most Americans are living paycheck to paycheck and not saving any money as justification for the brilliant (*cough*) myRA government savings plans so we felt that it would be prudent to take a deeper look at what ‘saving’ is.
You see, we don’t think that saving is about money. Money is involved, but it is not the focus. Saving is really about storing our productive efforts.
It goes back to the days of barter…
Back then the fisherman would catch extra fish in the morning and take them to the market in the afternoon to trade his extra fish with the farmer for vegetables. His wife liked to have vegetables with her fish for supper so he had to trade for vegetables instead of the painted rock that he really liked.
The fisherman had learned that fish would start to smell bad the day after being caught so he had no choice but to trade all of his extra fish every afternoon and go fishing for more again every morning.
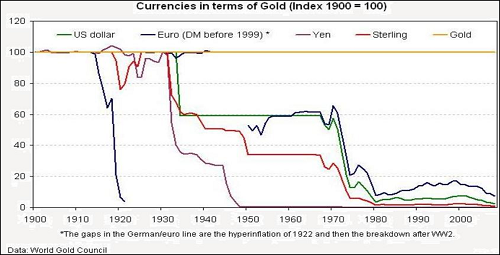
Until the fisherman discovered gold. Then the fisherman could trade his extra fish for gold and take the next day off. The fisherman didn’t really care about amassing gold; he just figured out that gold would let him store his production so he didn’t have to go fishing every single day to feed his family. And it turned out that three day old gold smelled much better than three day old fish – this was a bonus.
So saving was born!
Somewhere along the line we forgot this and started to think that saving was about amassing money. And on top of that we started to think that money was paper and not gold. We are so forgetful!
So when saving became about money and not about production we opened the door to debt. We started to think that instead of saving we could just borrow whatever money we needed. After all, the credit money still bought stuff just like the saved money except we didn’t have to wait to use it!
But then when we had to start using our entire paycheck to pay back all of the credit money we found out that we had to be even more productive now than before we went into debt. Our plan backfired.
We didn’t learn from our smart fisherman ancestor and now we had to go fishing both in the morning and in the afternoon to have enough fish for our supper and also enough to trade for vegetables so our wife won’t get mad and also enough to give to the banker to pay him back for the credit money that bought us the really neat painted rock.
Darn painted rocks.